Discrete¶
|
Binomial log-likelihood. |
|
Zero-inflated Binomial log-likelihood. |
|
Beta-binomial log-likelihood. |
|
Bernoulli log-likelihood |
|
Poisson log-likelihood. |
|
Zero-inflated Poisson log-likelihood. |
|
Negative binomial log-likelihood. |
|
Zero-Inflated Negative binomial log-likelihood. |
|
Discrete uniform distribution. |
|
Geometric log-likelihood. |
|
Categorical log-likelihood. |
|
Discrete Weibull log-likelihood |
|
Constant log-likelihood. |
|
Ordered Logistic log-likelihood. |
-
class
pymc3.distributions.discrete.Bernoulli(name, *args, **kwargs)¶ Bernoulli log-likelihood
The Bernoulli distribution describes the probability of successes (x=1) and failures (x=0). The pmf of this distribution is
\[f(x \mid p) = p^{x} (1-p)^{1-x}\](Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
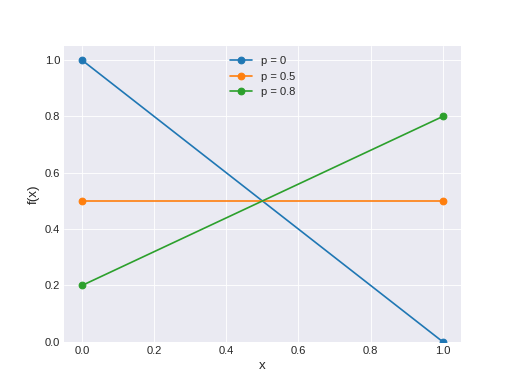
Support
\(x \in \{0, 1\}\)
Mean
\(p\)
Variance
\(p (1 - p)\)
- Parameters
- p: float
Probability of success (0 < p < 1).
- logit_p: float
Logit of success probability. Only one of p and logit_p can be specified.
-
logcdf(value)¶ Compute the log of the cumulative distribution function for Bernoulli distribution at the specified value.
- Parameters
- value: numeric or np.ndarray or theano.tensor
Value(s) for which log CDF is calculated. If the log CDF for multiple values are desired the values must be provided in a numpy array or theano tensor.
- Returns
- TensorVariable
-
logp(value)¶ Calculate log-probability of Bernoulli distribution at specified value.
- Parameters
- value: numeric
Value(s) for which log-probability is calculated. If the log probabilities for multiple values are desired the values must be provided in a numpy array or theano tensor
- Returns
- TensorVariable
-
random(point=None, size=None)¶ Draw random values from Bernoulli distribution.
- Parameters
- point: dict, optional
Dict of variable values on which random values are to be conditioned (uses default point if not specified).
- size: int, optional
Desired size of random sample (returns one sample if not specified).
- Returns
- array
-
class
pymc3.distributions.discrete.BetaBinomial(name, *args, **kwargs)¶ Beta-binomial log-likelihood.
Equivalent to binomial random variable with success probability drawn from a beta distribution. The pmf of this distribution is
\[f(x \mid \alpha, \beta, n) = \binom{n}{x} \frac{B(x + \alpha, n - x + \beta)}{B(\alpha, \beta)}\](Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
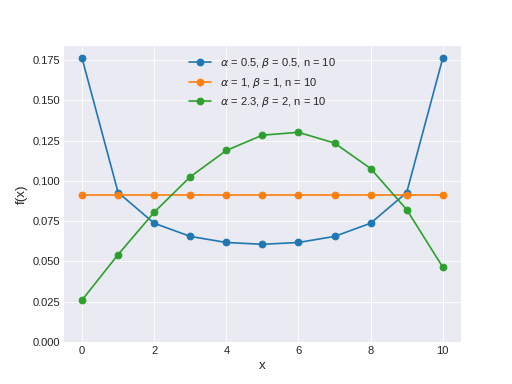
Support
\(x \in \{0, 1, \ldots, n\}\)
Mean
\(n \dfrac{\alpha}{\alpha + \beta}\)
Variance
\(n \dfrac{\alpha \beta}{(\alpha+\beta)^2 (\alpha+\beta+1)}\)
- Parameters
- n: int
Number of Bernoulli trials (n >= 0).
- alpha: float
alpha > 0.
- beta: float
beta > 0.
-
logcdf(value)¶ Compute the log of the cumulative distribution function for BetaBinomial distribution at the specified value.
- Parameters
- value: numeric
Value for which log CDF is calculated.
- Returns
- TensorVariable
-
logp(value)¶ Calculate log-probability of BetaBinomial distribution at specified value.
- Parameters
- value: numeric
Value(s) for which log-probability is calculated. If the log probabilities for multiple values are desired the values must be provided in a numpy array or theano tensor
- Returns
- TensorVariable
-
random(point=None, size=None)¶ Draw random values from BetaBinomial distribution.
- Parameters
- point: dict, optional
Dict of variable values on which random values are to be conditioned (uses default point if not specified).
- size: int, optional
Desired size of random sample (returns one sample if not specified).
- Returns
- array
-
class
pymc3.distributions.discrete.Binomial(name, *args, **kwargs)¶ Binomial log-likelihood.
The discrete probability distribution of the number of successes in a sequence of n independent yes/no experiments, each of which yields success with probability p. The pmf of this distribution is
\[f(x \mid n, p) = \binom{n}{x} p^x (1-p)^{n-x}\](Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
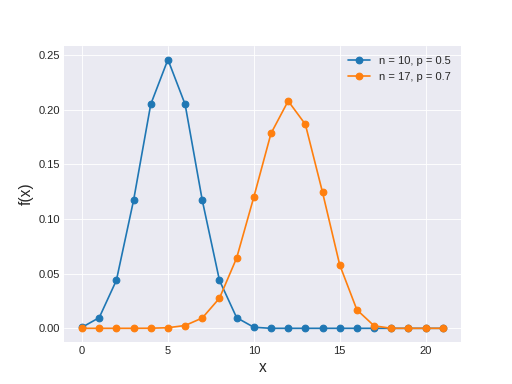
Support
\(x \in \{0, 1, \ldots, n\}\)
Mean
\(n p\)
Variance
\(n p (1 - p)\)
- Parameters
- n: int
Number of Bernoulli trials (n >= 0).
- p: float
Probability of success in each trial (0 < p < 1).
-
logcdf(value)¶ Compute the log of the cumulative distribution function for Binomial distribution at the specified value.
- Parameters
- value: numeric
Value for which log CDF is calculated.
- Returns
- TensorVariable
-
logp(value)¶ Calculate log-probability of Binomial distribution at specified value.
- Parameters
- value: numeric
Value(s) for which log-probability is calculated. If the log probabilities for multiple values are desired the values must be provided in a numpy array or theano tensor
- Returns
- TensorVariable
-
random(point=None, size=None)¶ Draw random values from Binomial distribution.
- Parameters
- point: dict, optional
Dict of variable values on which random values are to be conditioned (uses default point if not specified).
- size: int, optional
Desired size of random sample (returns one sample if not specified).
- Returns
- array
-
class
pymc3.distributions.discrete.Categorical(name, *args, **kwargs)¶ Categorical log-likelihood.
The most general discrete distribution. The pmf of this distribution is
\[f(x \mid p) = p_x\](Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
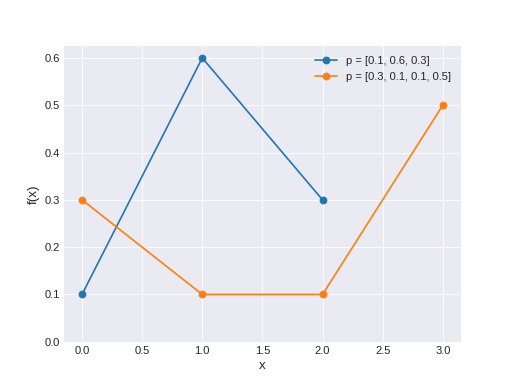
Support
\(x \in \{0, 1, \ldots, |p|-1\}\)
- Parameters
- p: array of floats
p > 0 and the elements of p must sum to 1. They will be automatically rescaled otherwise.
-
logp(value)¶ Calculate log-probability of Categorical distribution at specified value.
- Parameters
- value: numeric
Value(s) for which log-probability is calculated. If the log probabilities for multiple values are desired the values must be provided in a numpy array or theano tensor
- Returns
- TensorVariable
-
random(point=None, size=None)¶ Draw random values from Categorical distribution.
- Parameters
- point: dict, optional
Dict of variable values on which random values are to be conditioned (uses default point if not specified).
- size: int, optional
Desired size of random sample (returns one sample if not specified).
- Returns
- array
-
class
pymc3.distributions.discrete.Constant(name, *args, **kwargs)¶ Constant log-likelihood.
- Parameters
- value: float or int
Constant parameter.
-
logp(value)¶ Calculate log-probability of Constant distribution at specified value.
- Parameters
- value: numeric
Value(s) for which log-probability is calculated. If the log probabilities for multiple values are desired the values must be provided in a numpy array or theano tensor
- Returns
- TensorVariable
-
random(point=None, size=None)¶ Draw random values from Constant distribution.
- Parameters
- point: dict, optional
Dict of variable values on which random values are to be conditioned (uses default point if not specified).
- size: int, optional
Desired size of random sample (returns one sample if not specified).
- Returns
- array
-
pymc3.distributions.discrete.ConstantDist¶
-
class
pymc3.distributions.discrete.DiscreteUniform(name, *args, **kwargs)¶ Discrete uniform distribution. The pmf of this distribution is
\[f(x \mid lower, upper) = \frac{1}{upper-lower+1}\](Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
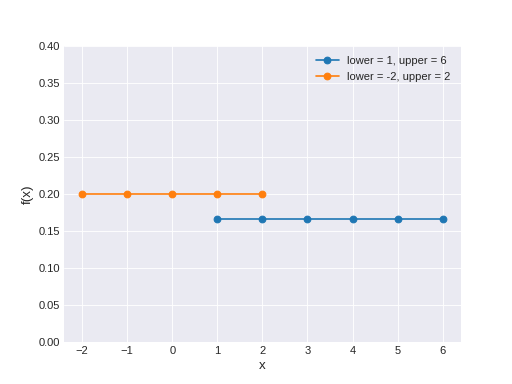
Support
\(x \in {lower, lower + 1, \ldots, upper}\)
Mean
\(\dfrac{lower + upper}{2}\)
Variance
\(\dfrac{(upper - lower)^2}{12}\)
- Parameters
- lower: int
Lower limit.
- upper: int
Upper limit (upper > lower).
-
logcdf(value)¶ Compute the log of the cumulative distribution function for Discrete uniform distribution at the specified value.
- Parameters
- value: numeric or np.ndarray or theano.tensor
Value(s) for which log CDF is calculated. If the log CDF for multiple values are desired the values must be provided in a numpy array or theano tensor.
- Returns
- TensorVariable
-
logp(value)¶ Calculate log-probability of DiscreteUniform distribution at specified value.
- Parameters
- value: numeric
Value(s) for which log-probability is calculated. If the log probabilities for multiple values are desired the values must be provided in a numpy array or theano tensor
- Returns
- TensorVariable
-
random(point=None, size=None)¶ Draw random values from DiscreteUniform distribution.
- Parameters
- point: dict, optional
Dict of variable values on which random values are to be conditioned (uses default point if not specified).
- size: int, optional
Desired size of random sample (returns one sample if not specified).
- Returns
- array
-
class
pymc3.distributions.discrete.DiscreteWeibull(name, *args, **kwargs)¶ Discrete Weibull log-likelihood
The discrete Weibull distribution is a flexible model of count data that can handle both over- and under-dispersion. The pmf of this distribution is
\[f(x \mid q, \beta) = q^{x^{\beta}} - q^{(x + 1)^{\beta}}\](Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
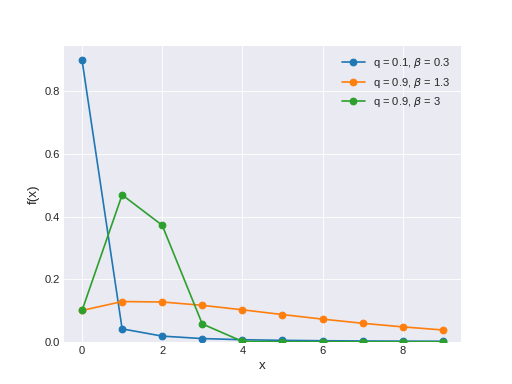
Support
\(x \in \mathbb{N}_0\)
Mean
\(\mu = \sum_{x = 1}^{\infty} q^{x^{\beta}}\)
Variance
\(2 \sum_{x = 1}^{\infty} x q^{x^{\beta}} - \mu - \mu^2\)
-
logcdf(value)¶ Compute the log of the cumulative distribution function for Discrete Weibull distribution at the specified value.
- Parameters
- value: numeric or np.ndarray or theano.tensor
Value(s) for which log CDF is calculated. If the log CDF for multiple values are desired the values must be provided in a numpy array or theano tensor.
- Returns
- TensorVariable
-
logp(value)¶ Calculate log-probability of DiscreteWeibull distribution at specified value.
- Parameters
- value: numeric
Value(s) for which log-probability is calculated. If the log probabilities for multiple values are desired the values must be provided in a numpy array or theano tensor
- Returns
- TensorVariable
-
random(point=None, size=None)¶ Draw random values from DiscreteWeibull distribution.
- Parameters
- point: dict, optional
Dict of variable values on which random values are to be conditioned (uses default point if not specified).
- size: int, optional
Desired size of random sample (returns one sample if not specified).
- Returns
- array
-
-
class
pymc3.distributions.discrete.Geometric(name, *args, **kwargs)¶ Geometric log-likelihood.
The probability that the first success in a sequence of Bernoulli trials occurs on the x’th trial. The pmf of this distribution is
\[f(x \mid p) = p(1-p)^{x-1}\](Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
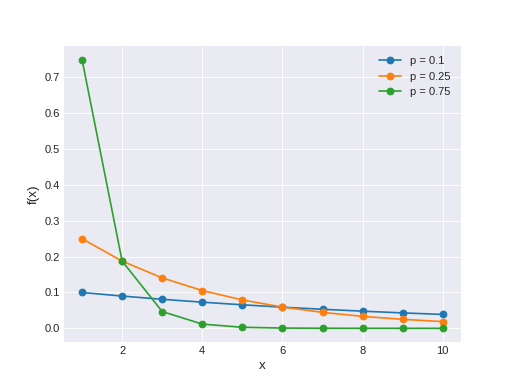
Support
\(x \in \mathbb{N}_{>0}\)
Mean
\(\dfrac{1}{p}\)
Variance
\(\dfrac{1 - p}{p^2}\)
- Parameters
- p: float
Probability of success on an individual trial (0 < p <= 1).
-
logcdf(value)¶ Compute the log of the cumulative distribution function for Geometric distribution at the specified value.
- Parameters
- value: numeric or np.ndarray or theano.tensor
Value(s) for which log CDF is calculated. If the log CDF for multiple values are desired the values must be provided in a numpy array or theano tensor.
- Returns
- TensorVariable
-
logp(value)¶ Calculate log-probability of Geometric distribution at specified value.
- Parameters
- value: numeric
Value(s) for which log-probability is calculated. If the log probabilities for multiple values are desired the values must be provided in a numpy array or theano tensor
- Returns
- TensorVariable
-
random(point=None, size=None)¶ Draw random values from Geometric distribution.
- Parameters
- point: dict, optional
Dict of variable values on which random values are to be conditioned (uses default point if not specified).
- size: int, optional
Desired size of random sample (returns one sample if not specified).
- Returns
- array
-
class
pymc3.distributions.discrete.HyperGeometric(name, *args, **kwargs)¶ Discrete hypergeometric distribution.
The probability of \(x\) successes in a sequence of \(n\) bernoulli trials taken without replacement from a population of \(N\) objects, containing \(k\) good (or successful or Type I) objects. The pmf of this distribution is
\[f(x \mid N, n, k) = \frac{\binom{k}{x}\binom{N-k}{n-x}}{\binom{N}{n}}\](Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
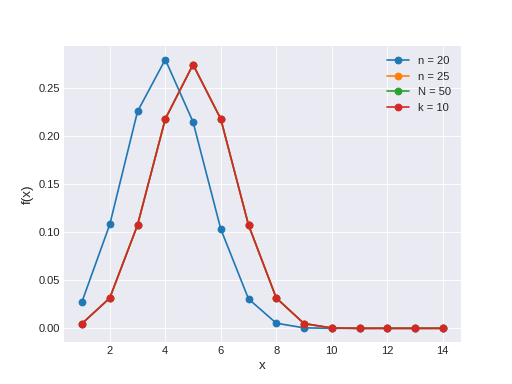
Support
\(x \in \left[\max(0, n - N + k), \min(k, n)\right]\)
Mean
\(\dfrac{nk}{N}\)
Variance
\(\dfrac{(N-n)nk(N-k)}{(N-1)N^2}\)
- Parameters
- Ninteger
Total size of the population
- kinteger
Number of successful individuals in the population
- ninteger
Number of samples drawn from the population
-
logcdf(value)¶ Compute the log of the cumulative distribution function for HyperGeometric distribution at the specified value.
- Parameters
- value: numeric
Value for which log CDF is calculated.
- Returns
- TensorVariable
-
logp(value)¶ Calculate log-probability of HyperGeometric distribution at specified value.
- Parameters
- valuenumeric
Value(s) for which log-probability is calculated. If the log probabilities for multiple values are desired the values must be provided in a numpy array or theano tensor
- Returns
- TensorVariable
-
random(point=None, size=None)¶ Draw random values from HyperGeometric distribution.
- Parameters
- pointdict, optional
Dict of variable values on which random values are to be conditioned (uses default point if not specified).
- sizeint, optional
Desired size of random sample (returns one sample if not specified).
- Returns
- array
-
class
pymc3.distributions.discrete.NegativeBinomial(name, *args, **kwargs)¶ Negative binomial log-likelihood.
The negative binomial distribution describes a Poisson random variable whose rate parameter is gamma distributed. The pmf of this distribution is
\[f(x \mid \mu, \alpha) = \binom{x + \alpha - 1}{x} (\alpha/(\mu+\alpha))^\alpha (\mu/(\mu+\alpha))^x\](Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
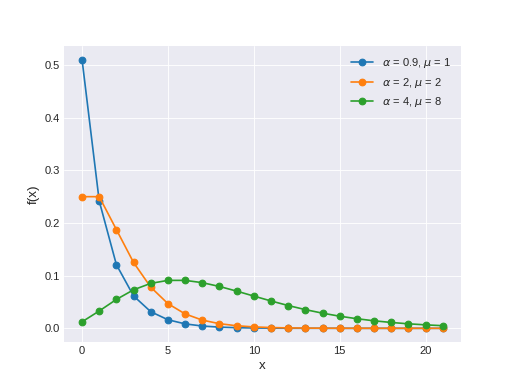
Support
\(x \in \mathbb{N}_0\)
Mean
\(\mu\)
The negative binomial distribution can be parametrized either in terms of mu or p, and either in terms of alpha or n. The link between the parametrizations is given by
\[\begin{split}\mu &= \frac{n(1-p)}{p} \\ \alpha &= n\end{split}\]- Parameters
- mu: float
Poission distribution parameter (mu > 0).
- alpha: float
Gamma distribution parameter (alpha > 0).
- p: float
Alternative probability of success in each trial (0 < p < 1).
- n: float
Alternative number of target success trials (n > 0)
-
logcdf(value)¶ Compute the log of the cumulative distribution function for NegativeBinomial distribution at the specified value.
- Parameters
- value: numeric
Value for which log CDF is calculated.
- Returns
- TensorVariable
-
logp(value)¶ Calculate log-probability of NegativeBinomial distribution at specified value.
- Parameters
- value: numeric
Value(s) for which log-probability is calculated. If the log probabilities for multiple values are desired the values must be provided in a numpy array or theano tensor
- Returns
- TensorVariable
-
random(point=None, size=None)¶ Draw random values from NegativeBinomial distribution.
- Parameters
- point: dict, optional
Dict of variable values on which random values are to be conditioned (uses default point if not specified).
- size: int, optional
Desired size of random sample (returns one sample if not specified).
- Returns
- array
-
class
pymc3.distributions.discrete.OrderedLogistic(name, *args, **kwargs)¶ Ordered Logistic log-likelihood.
Useful for regression on ordinal data values whose values range from 1 to K as a function of some predictor, \(\eta\). The cutpoints, \(c\), separate which ranges of \(\eta\) are mapped to which of the K observed dependent variables. The number of cutpoints is K - 1. It is recommended that the cutpoints are constrained to be ordered.
\[\begin{split}f(k \mid \eta, c) = \left\{ \begin{array}{l} 1 - \text{logit}^{-1}(\eta - c_1) \,, \text{if } k = 0 \\ \text{logit}^{-1}(\eta - c_{k - 1}) - \text{logit}^{-1}(\eta - c_{k}) \,, \text{if } 0 < k < K \\ \text{logit}^{-1}(\eta - c_{K - 1}) \,, \text{if } k = K \\ \end{array} \right.\end{split}\]- Parameters
- eta: float
The predictor.
- c: array
The length K - 1 array of cutpoints which break \(\eta\) into ranges. Do not explicitly set the first and last elements of \(c\) to negative and positive infinity.
Examples
# Generate data for a simple 1 dimensional example problem n1_c = 300; n2_c = 300; n3_c = 300 cluster1 = np.random.randn(n1_c) + -1 cluster2 = np.random.randn(n2_c) + 0 cluster3 = np.random.randn(n3_c) + 2 x = np.concatenate((cluster1, cluster2, cluster3)) y = np.concatenate((1*np.ones(n1_c), 2*np.ones(n2_c), 3*np.ones(n3_c))) - 1 # Ordered logistic regression with pm.Model() as model: cutpoints = pm.Normal("cutpoints", mu=[-1,1], sigma=10, shape=2, transform=pm.distributions.transforms.ordered) y_ = pm.OrderedLogistic("y", cutpoints=cutpoints, eta=x, observed=y) tr = pm.sample(1000) # Plot the results plt.hist(cluster1, 30, alpha=0.5); plt.hist(cluster2, 30, alpha=0.5); plt.hist(cluster3, 30, alpha=0.5); plt.hist(tr["cutpoints"][:,0], 80, alpha=0.2, color='k'); plt.hist(tr["cutpoints"][:,1], 80, alpha=0.2, color='k');
-
class
pymc3.distributions.discrete.Poisson(name, *args, **kwargs)¶ Poisson log-likelihood.
Often used to model the number of events occurring in a fixed period of time when the times at which events occur are independent. The pmf of this distribution is
\[f(x \mid \mu) = \frac{e^{-\mu}\mu^x}{x!}\](Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
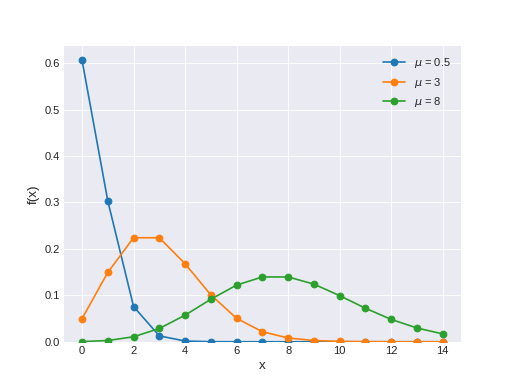
Support
\(x \in \mathbb{N}_0\)
Mean
\(\mu\)
Variance
\(\mu\)
- Parameters
- mu: float
Expected number of occurrences during the given interval (mu >= 0).
Notes
The Poisson distribution can be derived as a limiting case of the binomial distribution.
-
logcdf(value)¶ Compute the log of the cumulative distribution function for Poisson distribution at the specified value.
- Parameters
- value: numeric or np.ndarray or theano.tensor
Value(s) for which log CDF is calculated. If the log CDF for multiple values are desired the values must be provided in a numpy array or theano tensor.
- Returns
- TensorVariable
-
logp(value)¶ Calculate log-probability of Poisson distribution at specified value.
- Parameters
- value: numeric
Value(s) for which log-probability is calculated. If the log probabilities for multiple values are desired the values must be provided in a numpy array or theano tensor
- Returns
- TensorVariable
-
random(point=None, size=None)¶ Draw random values from Poisson distribution.
- Parameters
- point: dict, optional
Dict of variable values on which random values are to be conditioned (uses default point if not specified).
- size: int, optional
Desired size of random sample (returns one sample if not specified).
- Returns
- array
-
class
pymc3.distributions.discrete.ZeroInflatedBinomial(name, *args, **kwargs)¶ Zero-inflated Binomial log-likelihood.
The pmf of this distribution is
\[\begin{split}f(x \mid \psi, n, p) = \left\{ \begin{array}{l} (1-\psi) + \psi (1-p)^{n}, \text{if } x = 0 \\ \psi {n \choose x} p^x (1-p)^{n-x}, \text{if } x=1,2,3,\ldots,n \end{array} \right.\end{split}\](Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
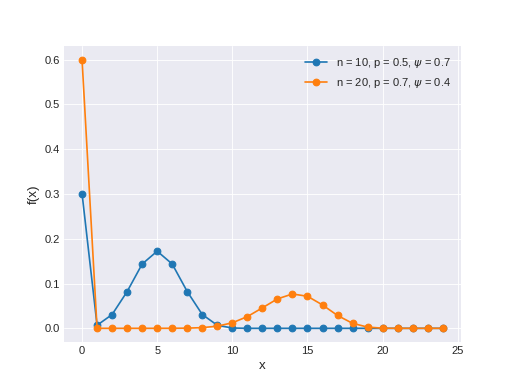
Support
\(x \in \mathbb{N}_0\)
Mean
\((1 - \psi) n p\)
Variance
\((1-\psi) n p [1 - p(1 - \psi n)].\)
- Parameters
- psi: float
Expected proportion of Binomial variates (0 < psi < 1)
- n: int
Number of Bernoulli trials (n >= 0).
- p: float
Probability of success in each trial (0 < p < 1).
-
logcdf(value)¶ Compute the log of the cumulative distribution function for ZeroInflatedBinomial distribution at the specified value.
- Parameters
- value: numeric
Value for which log CDF is calculated.
- Returns
- TensorVariable
-
logp(value)¶ Calculate log-probability of ZeroInflatedBinomial distribution at specified value.
- Parameters
- value: numeric
Value(s) for which log-probability is calculated. If the log probabilities for multiple values are desired the values must be provided in a numpy array or theano tensor
- Returns
- TensorVariable
-
random(point=None, size=None)¶ Draw random values from ZeroInflatedBinomial distribution.
- Parameters
- point: dict, optional
Dict of variable values on which random values are to be conditioned (uses default point if not specified).
- size: int, optional
Desired size of random sample (returns one sample if not specified).
- Returns
- array
-
class
pymc3.distributions.discrete.ZeroInflatedNegativeBinomial(name, *args, **kwargs)¶ Zero-Inflated Negative binomial log-likelihood.
The Zero-inflated version of the Negative Binomial (NB). The NB distribution describes a Poisson random variable whose rate parameter is gamma distributed. The pmf of this distribution is
\[\begin{split}f(x \mid \psi, \mu, \alpha) = \left\{ \begin{array}{l} (1-\psi) + \psi \left ( \frac{\alpha}{\alpha+\mu} \right) ^\alpha, \text{if } x = 0 \\ \psi \frac{\Gamma(x+\alpha)}{x! \Gamma(\alpha)} \left ( \frac{\alpha}{\mu+\alpha} \right)^\alpha \left( \frac{\mu}{\mu+\alpha} \right)^x, \text{if } x=1,2,3,\ldots \end{array} \right.\end{split}\](Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
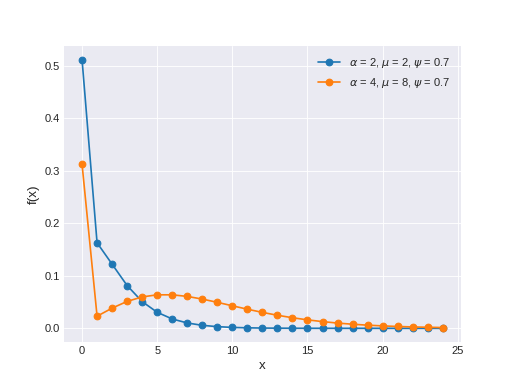
Support
\(x \in \mathbb{N}_0\)
Mean
\(\psi\mu\)
Var
\(\psi\mu + \left (1 + \frac{\mu}{\alpha} + \frac{1-\psi}{\mu} \right)\)
- Parameters
- psi: float
Expected proportion of NegativeBinomial variates (0 < psi < 1)
- mu: float
Poission distribution parameter (mu > 0).
- alpha: float
Gamma distribution parameter (alpha > 0).
-
logcdf(value)¶ Compute the log of the cumulative distribution function for ZeroInflatedNegativeBinomial distribution at the specified value.
- Parameters
- value: numeric
Value for which log CDF is calculated.
- Returns
- TensorVariable
-
logp(value)¶ Calculate log-probability of ZeroInflatedNegativeBinomial distribution at specified value.
- Parameters
- value: numeric
Value(s) for which log-probability is calculated. If the log probabilities for multiple values are desired the values must be provided in a numpy array or theano tensor
- Returns
- TensorVariable
-
random(point=None, size=None)¶ Draw random values from ZeroInflatedNegativeBinomial distribution.
- Parameters
- point: dict, optional
Dict of variable values on which random values are to be conditioned (uses default point if not specified).
- size: int, optional
Desired size of random sample (returns one sample if not specified).
- Returns
- array
-
class
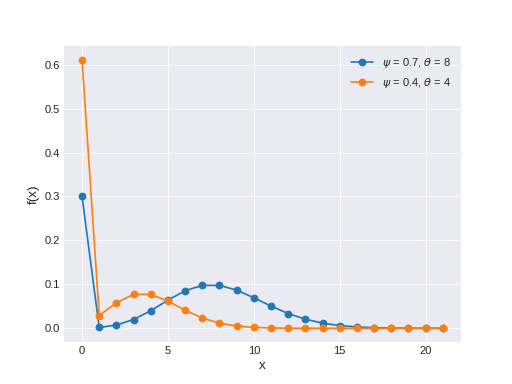
pymc3.distributions.discrete.ZeroInflatedPoisson(name, *args, **kwargs)¶ Zero-inflated Poisson log-likelihood.
Often used to model the number of events occurring in a fixed period of time when the times at which events occur are independent. The pmf of this distribution is
\[\begin{split}f(x \mid \psi, \theta) = \left\{ \begin{array}{l} (1-\psi) + \psi e^{-\theta}, \text{if } x = 0 \\ \psi \frac{e^{-\theta}\theta^x}{x!}, \text{if } x=1,2,3,\ldots \end{array} \right.\end{split}\](Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
Support
\(x \in \mathbb{N}_0\)
Mean
\(\psi\theta\)
Variance
\(\theta + \frac{1-\psi}{\psi}\theta^2\)
- Parameters
- psi: float
Expected proportion of Poisson variates (0 < psi < 1)
- theta: float
Expected number of occurrences during the given interval (theta >= 0).
-
logcdf(value)¶ Compute the log of the cumulative distribution function for ZeroInflatedPoisson distribution at the specified value.
- Parameters
- value: numeric or np.ndarray or theano.tensor
Value(s) for which log CDF is calculated. If the log CDF for multiple values are desired the values must be provided in a numpy array or theano tensor.
- Returns
- TensorVariable
-
logp(value)¶ Calculate log-probability of ZeroInflatedPoisson distribution at specified value.
- Parameters
- value: numeric
Value(s) for which log-probability is calculated. If the log probabilities for multiple values are desired the values must be provided in a numpy array or theano tensor
- Returns
- TensorVariable
-
random(point=None, size=None)¶ Draw random values from ZeroInflatedPoisson distribution.
- Parameters
- point: dict, optional
Dict of variable values on which random values are to be conditioned (uses default point if not specified).
- size: int, optional
Desired size of random sample (returns one sample if not specified).
- Returns
- array
